Prehospital Programs
High-performance CPR saves lives. Prehospital and public safety programs are based on the successful 10-step foundation developed by the Resuscitation Academy. This approach is proven to increase out-of-hospital cardiac arrest survival rates. The American Heart Association, Resuscitation Academy and Laerdal Medical have collaborated to improve cardiac arrest survival.
RQI Partners’ Resuscitation Quality Improvement programs are designed to optimize each element in the Chain of Survival. Blending the education, training technology and simulation expertise of Laerdal Medical, the resuscitation science leadership of the American Heart Association, and the hands-on experience of the Resuscitation Academy, these programs are designed to challenge the status quo, foster new ways of thinking about out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, and send more patients home.
10 Steps for Improving Survival from Cardiac Arrest
Using the steps outlined in the Resuscitation Academy’s book “10 Steps for Improving Survival From Cardiac Arrest,” many communities nationwide are demonstrating a successful approach to continuously improving survival from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA).
Steps one through four are foundational to this success due to their ability to measure system effectiveness and improve the quality of the first 10 minutes (600 seconds) of a cardiac arrest incident.

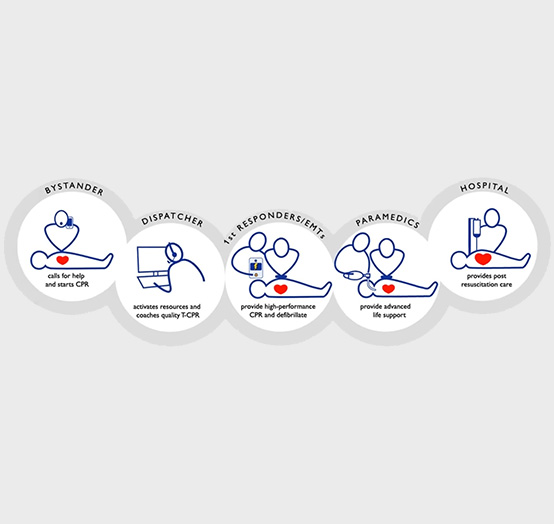
Chain of Survival
Roughly 350,000 out-of-hospital cardiac arrests occur each year in the U.S. An estimated 70-90% of patients die before reaching a hospital.1 The Chain of Survival illustrates a systems approach to saving more lives. Successful treatment of cardiac arrest — particularly ventricular fibrillation — is associated with an EMS system’s ability to deliver care quickly when it arrives at the scene. A strong Chain of Survival helps improve cardiac arrest victims’ chances of survival and recovery.
How Communities Can Improve Chances of Survival
When implemented and adapted locally, the 10 steps optimize a community’s Chain of Survival. When each link in the Chain of Survival is strengthened, survival conditions improve, saving lives. According to the Utstein template that measures cardiac arrest survival, the number of these patients who survive through hospital discharge determines a community’s cardiac arrest save rate.

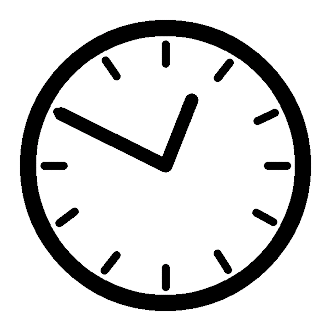
SECONDS
The First 600 Seconds Are Critical
A patient in cardiac arrest has just 600 seconds before death becomes irreversible. Every second without CPR decreases a cardiac arrest victim’s chance of survival. That’s why emergency telecommunicators’ actions can mean the difference between life and death.
The most effective way to increase bystander CPR rates is by providing real-time CPR instructions to 911 callers.

Telecommunicator CPR (T-CPR)
Telecommunicator CPR (T-CPR) is a low-dose, high-frequency, blended-learning quality improvement program designed to improve competency and performance in delivering T-CPR.
The T-CPR program gives emergency telecommunicators the tools they need to improve the quality of care they deliver to a patient in cardiac arrest. Based on the American Heart Association (AHA) science, including the resuscitation education guidelines, a turn-key solution allows for the rapid implementation of the AHA’s evidence-based T-CPR program, eliminating the manpower and costs associated with internal program development, delivery, and maintenance.
The T-CPR Essentials course offering is now available for purchase on ShopCPR. Designed for single use and delivered to learners online, the course allows telecommunicators to complete the four hours of T-CPR training while on duty at a console, eliminating impacts on staffing or overtime often associated with training. Topics include understanding the first 600 seconds, identifying cardiac arrest, coaching high-quality telephone CPR, caller management and special circumstances in resuscitation.
RQI for EMS
RQI for EMS includes tailored programs to verify competence and increase survival rates from sudden cardiac arrest. By focusing on mastery learning with verified skills competence, RQI for EMS helps reduce the overall cost of training while improving performance. RQI for EMS shifts from a traditional two-year resuscitation training mindset to one of mastery learning with verified skills competence. The program’s blended learning approach focuses on high-quality CPR to improve patient outcomes. Participants receive a verified BLS Provider eCredential and CME/CE.

RQI for Teams: Prehospital
Based on the legacy and success of the Resuscitation Academy high-performance CPR program, RQI for Teams: Prehospital is designed for those who respond to medical emergencies as a team.
RQI for Teams: Prehospital builds on the foundation of individual skills to maximize the effectiveness of a team response. The program employs low-dose, high frequency learning to improve outcomes in cardiac arrest calls.
Program content can be delivered via integration with an existing LMS or through the RQI 1Stop learning platform.
Communities Improving Cardiac Arrest Survival with the 10 Steps
When implemented and adapted locally, the 10 steps optimize a community’s Chain of Survival. These are just a few of the many communities seeing improved cardiac arrest survival rates.
Charles County
Maryland’s Charles County is the first community in the United States to pilot and adopt resuscitation quality improvement programs to advance prehospital response to cardiac arrest.
Its median response time for a cardiac arrest call is 5:24, and the incidence of bystander CPR before arrival is 27.4%. Its overall cardiac arrest survival rate is 8.6%, while the Utstein survival rate is 36.4%.
King County
Cardiac arrest victims are two to three times more likely to survive in Seattle, Washington, and nearby King County than in other communities. According to the EMS Division’s 2022 Annual Report to the King County Council, 242 lives were saved from OCHA in 2021. Its current five-year cumulative Utstein survival rate is 54%.
Hilton Head Island Fire Rescue
Hilton Head Island Fire Rescue responds to about 50 “workable” cardiac arrests annually. In 2017, Hilton Head Island Fire Rescue responded to 16 witnessed/shockable cardiac arrests, and 11 survived to the hospital. That put its survival rate at 68.75% for the year — one of the highest in the nation.



